Acrylic Vs PVC Plastic
What is Acrylic Plastic
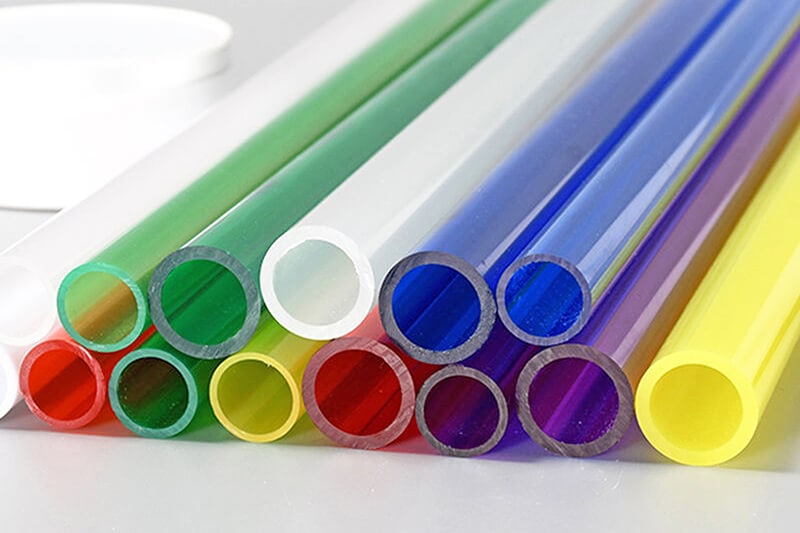
Acrylic sheet is a plastic material with outstanding strength, stiffness, optical clarity, and impact resistance. Acrylic sheets have 17 times more impact resistance than glass. Unlike glass, acrylic plastic needs a lot of force to shatter, so you don’t need to worry about damage to your acrylic.
This plastic material is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. And because of its versatility and wide range of applications, people from all around the world frequently use it as a go-to material.
Acrylic comes from natural gas (C5O2H8) and is completely inert when in solid form. So they do not turn yellow when they have been in contact with the sunlight for long. Acrylic can be used for greenhouses and many other roofing/sheeting purposes, which we will know in detail in the latter part of the content.
For more information about acrylic material, please see this blog.
What is PVC Plastic
PVC plastic (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a high-strength thermoplastic material commonly used for manufacturing different parts of instruments like pipes, medical devices, wire and cable insulation, etc.
PVC plastic is the world’s 3rd most produced synthetic plastic polymer. This material shows outstanding performance while being used for manufacturing other materials or tools. However, this has some drawbacks too.
PVC plastic is not heat-resistant enough. You need to be aware while machining a PVC plastic because this can resist heat up to 185° F. However, the durability and quality of PVC plastics in building materials are worth appreciation.
Differences Between Acrylic and PVC Plastic
Applications of Acrylic
Applications of PVC Plastic
Properties of Acrylic
Properties of PVC
Acrylic Vs PVC Kitchen Laminating
The high reflective gloss of acrylic laminating can provide you a smooth look in the kitchen cabinetries. It is also available in a wide variety of colors to make your kitchen just as you desire!
On the other hand, PVC laminate is composite artificial material commonly used in modular kitchens. The topmost layer is usually protected with decorative patterns or colors. Now let us know what difference these two make.
We prefer acrylic laminating for high-end kitchens. It makes the kitchen look more spacious. This attracts visitors to the outstanding design of your kitchen. On the other hand, PVC has various texture styles ranging from matte, glossy, natural, and wooden.
Acrylic finishes are more available in solid and vibrant colors. Compared to acrylic, PVC has a wider range of colors.
Acrylic finishes are scratch-resistant and do not decay over the years, but PVC laminating maintains a seamless and glossy appearance. Acrylic surfaces can be scratched with very sharp objects. One thing you need to consider is that the edges of PVC can be chipped if handled roughly.
Related Articles
Conclusion
Now that you know all about acrylic and PVC plastics, you can make your own decision. Both of them are machinable objects, but the selection depends on your needs. What material and what purpose do you need it for?
If it is for clarity and light transmission, you can choose acrylic as this provides better clarity. Different tools are designed with acrylic and PVC plastics.
For instance, think of a manifold; you can get a PVC manifold available on the market, but do you need it transparent? You need to choose a transparent manifold that only acrylic plastic can provide if you need to see the manifold’s inner mechanism. Still, confused about which one to buy? Don’t worry. Get in touch with us and let UV Acrylic help you decide the best material for your project.