Polycarbonate Plastic You Need To Know
Polycarbonate Plastic, the short name “PC”, was synthesized through chemical reactions between bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene COCl2. It was first patented in 1953 by Hermann Schnell at Bayer with the trademark “Makloron”. Also, in 1953, Daniel Fox at General Electric (GE) synthesized polycarbonate plastic, the trademark is “Lexan.”
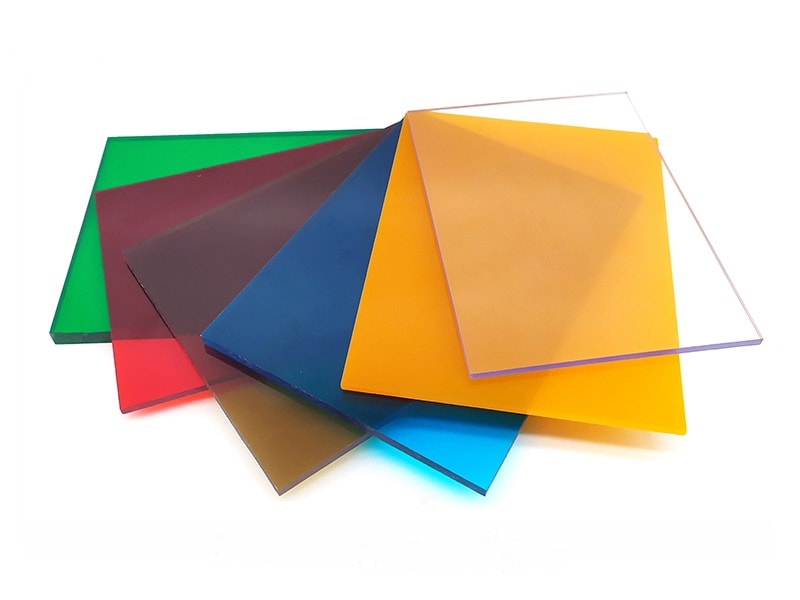
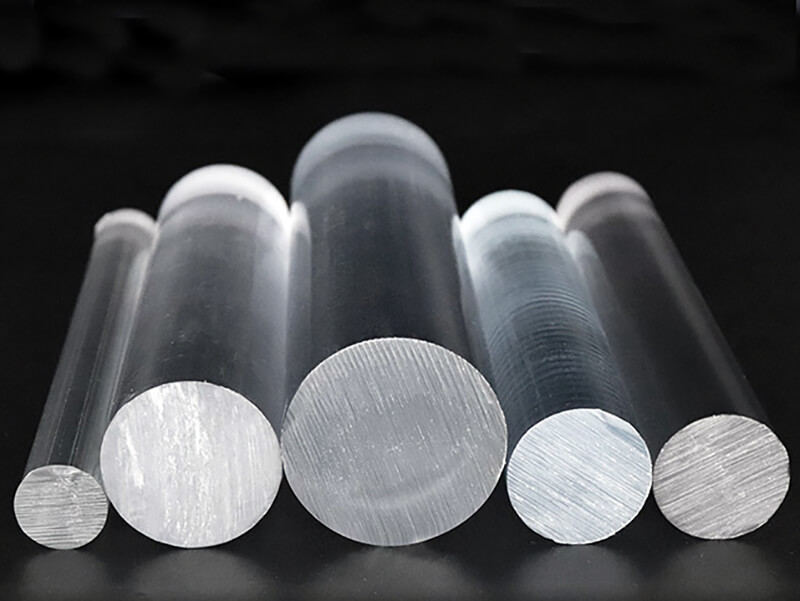
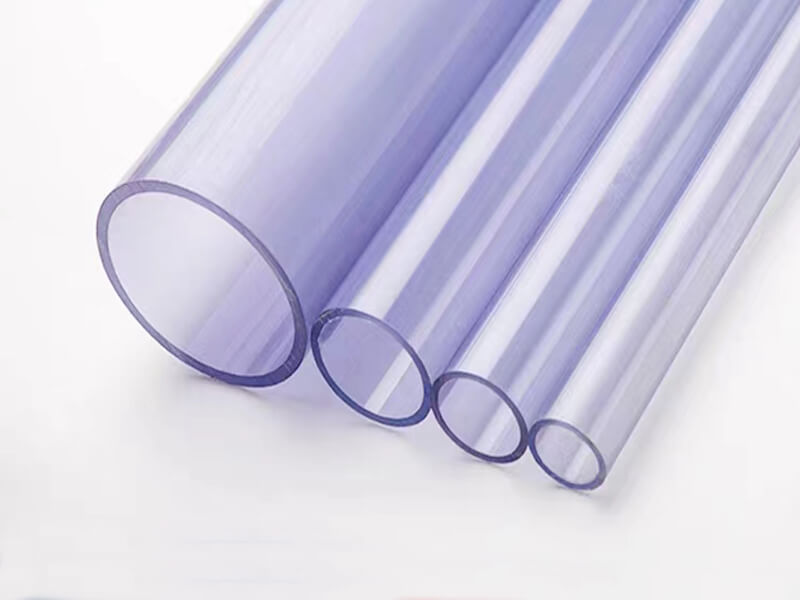
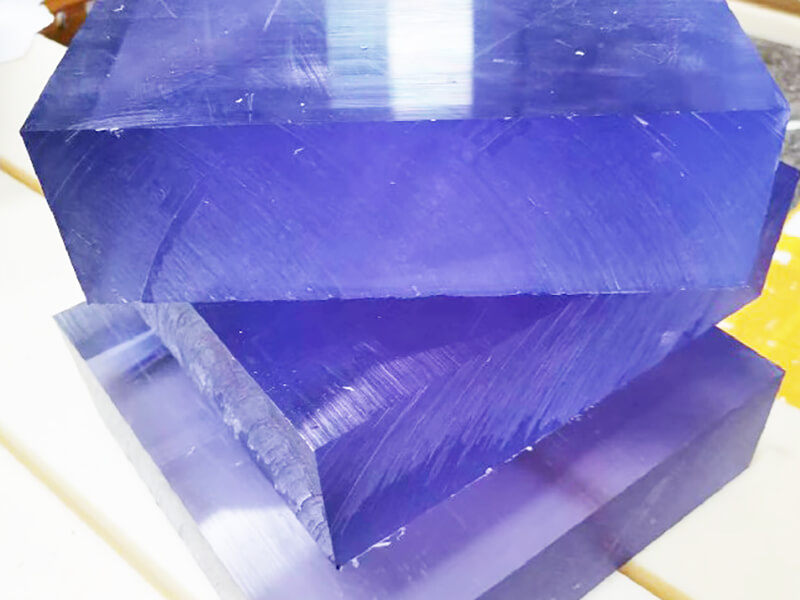
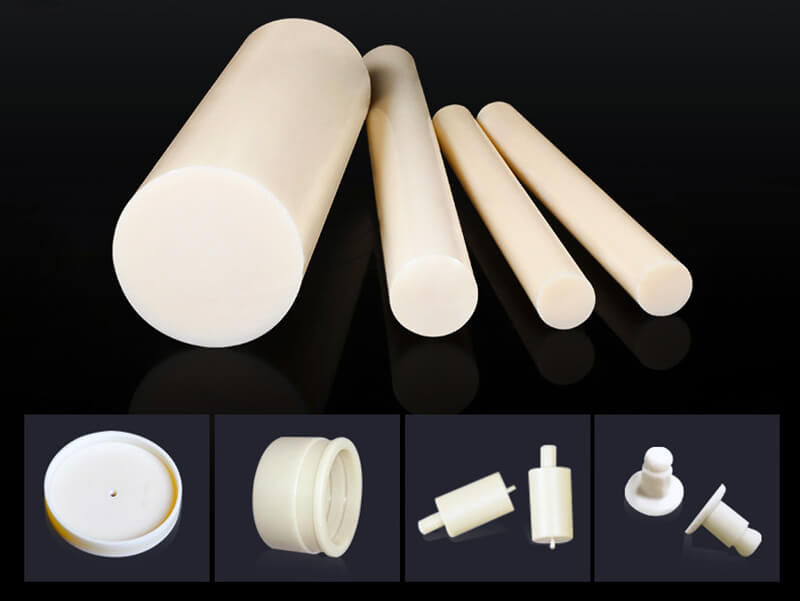
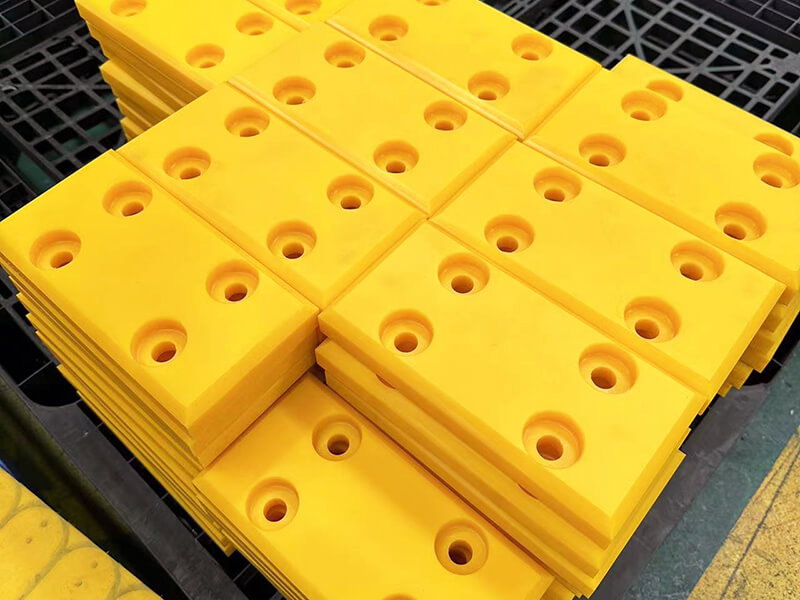
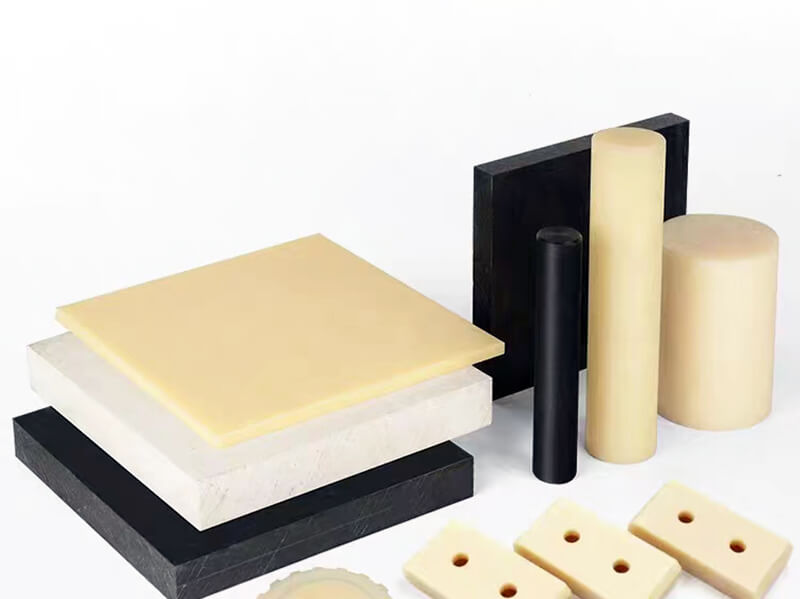
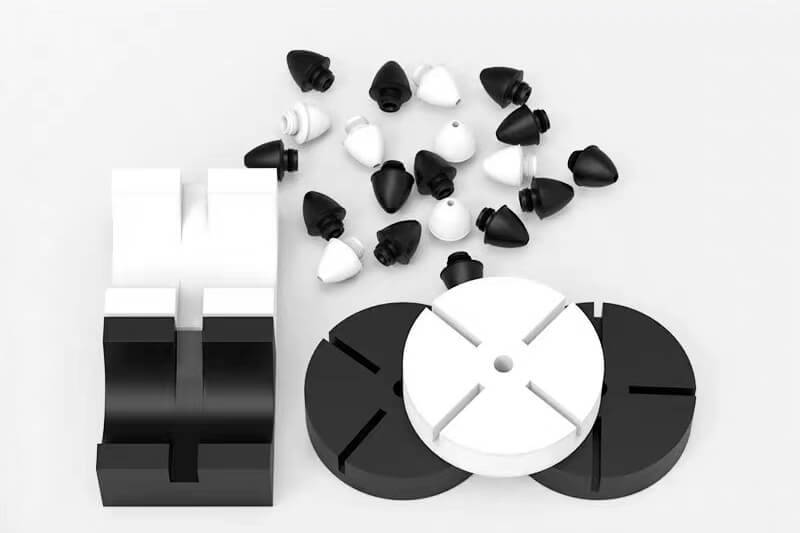
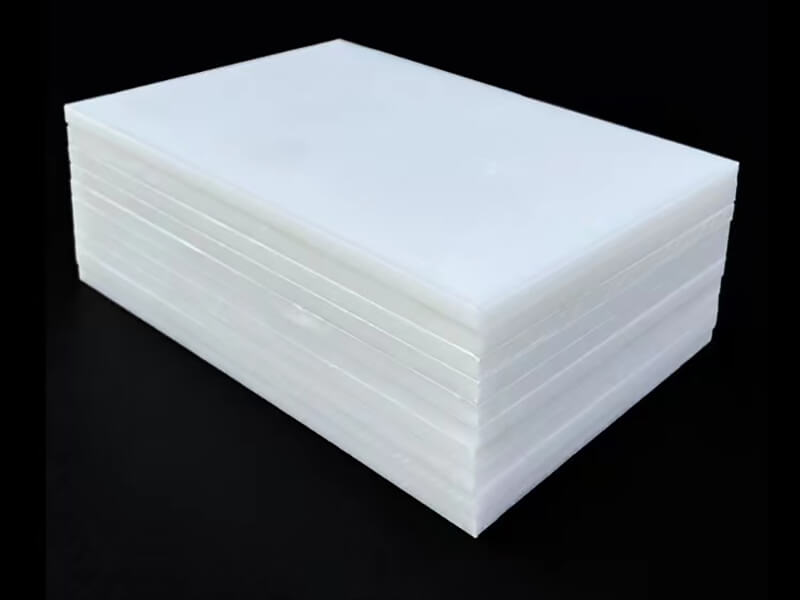
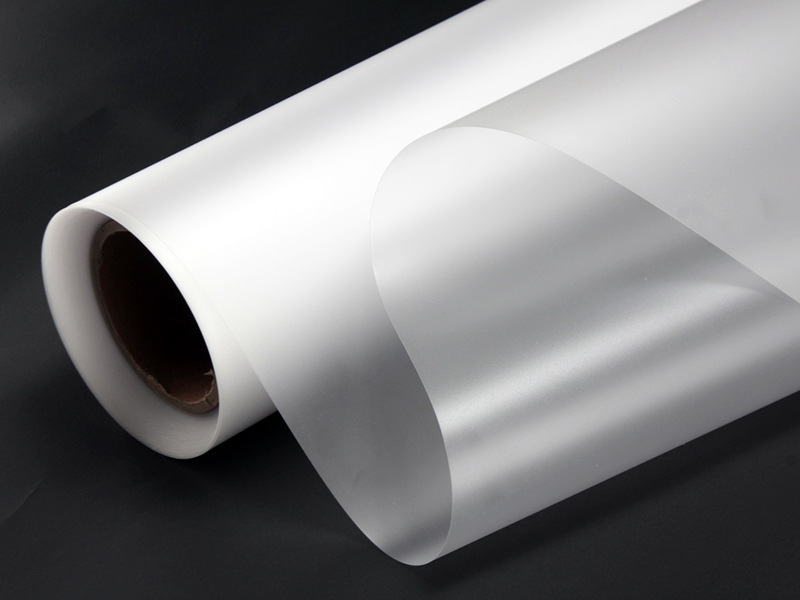
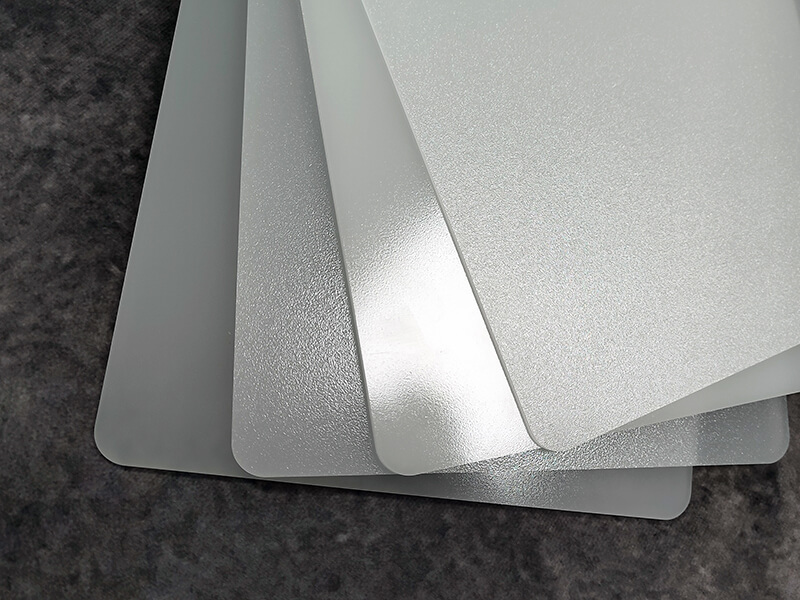
Polycarbonate Plastic is one of the thermoplastics, its main features include good optical properties, excellent impact resistance, and extraordinary durability. It can be extruded into panels, thin films, blocks, rods, tubes, and other plastic profiles with special shapes. Polycarbonate Plastic also can be injection molded into some plastic parts for industrial parts and components.
As one of the popular engineering plastics, Polycarbonate (PC) plastic is virtually unbreakable. It offers lightweight and high optical clarity, so it is widely used for window glass and roofing panels for buildings, front panels of screens, machine guards, signs, and plastic parts and components for industrial use.
Can’t find what you need? Or need a custom polycarbonate?
Leading Supplier of Polycarbonate Plastic In China
In 2003, UVTECO began manufacturing polycarbonate sheets/films/blocks/rods/tubes by using high-quality polycarbonate plastic from Sabic, Covestro, Teijin, etc. With continuous effort, UVTECO has grown to be a leading supplier of polycarbonate-based products in China, and we store polycarbonate films/sheets/blocks/rods/tubes in frequently used sizes for fast delivery.
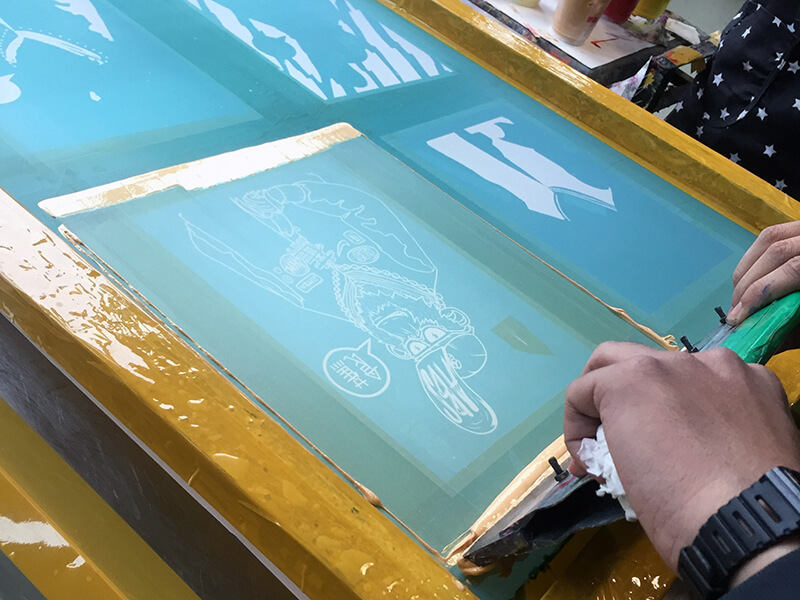
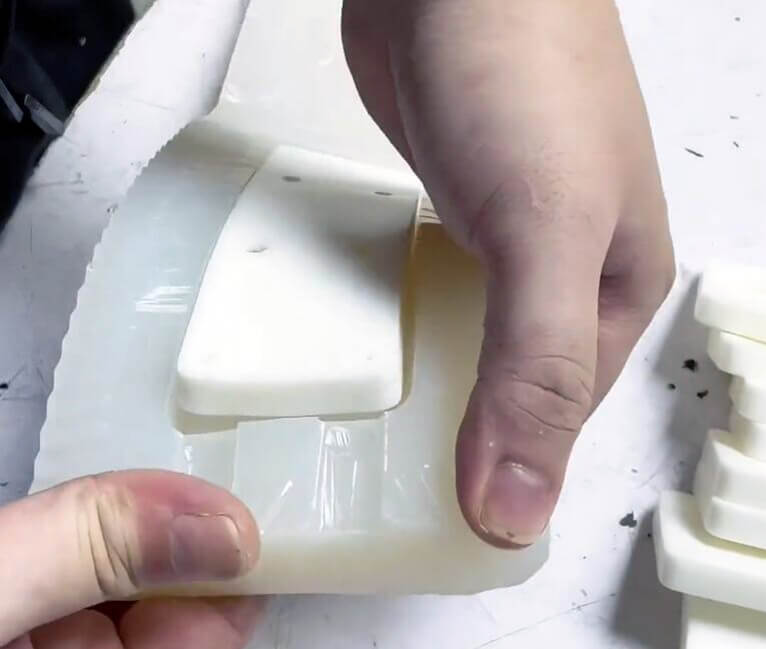
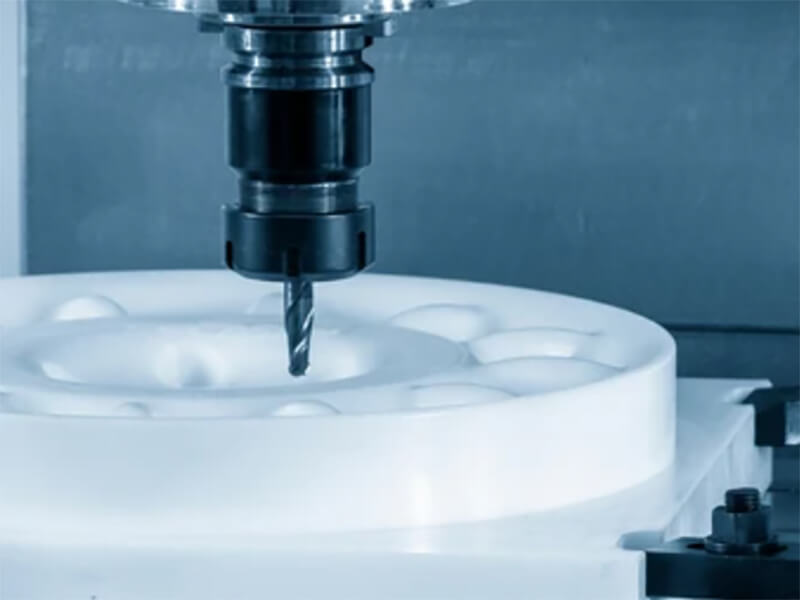
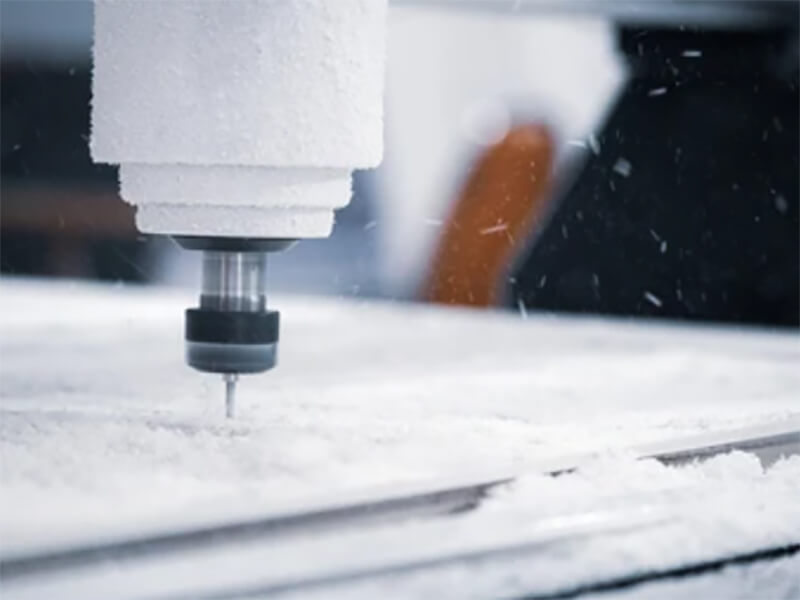
Otherwise, UVTECO can provide an integrated machining solution for polycarbonate-based parts/components. The main machining methods include cutting, bending, drilling, 3-axis and 5-axis CNC milling, CNC Turning, injection molding, thermal forming, silk-screen/UV printing, engraving, polishing, coating, etc.
Today, UVTECO provides high-quality polycarbonate-based products/parts/components for more than 2,500 clients from more than 45 countries. They work in agriculture, architecture, automation, the automobile industry, the medical industry, the aerospace industry, security, protection, etc.
Contact UVTECO for machining Polycarbonate service
Related Blogs about Polycarbonate Plastic
Frequently Asked Questions about Polycarbonate Plastic

Contact UVTECO
Have questions or need help? Fill out the right form, we will be in touch with you as quickly as possible.