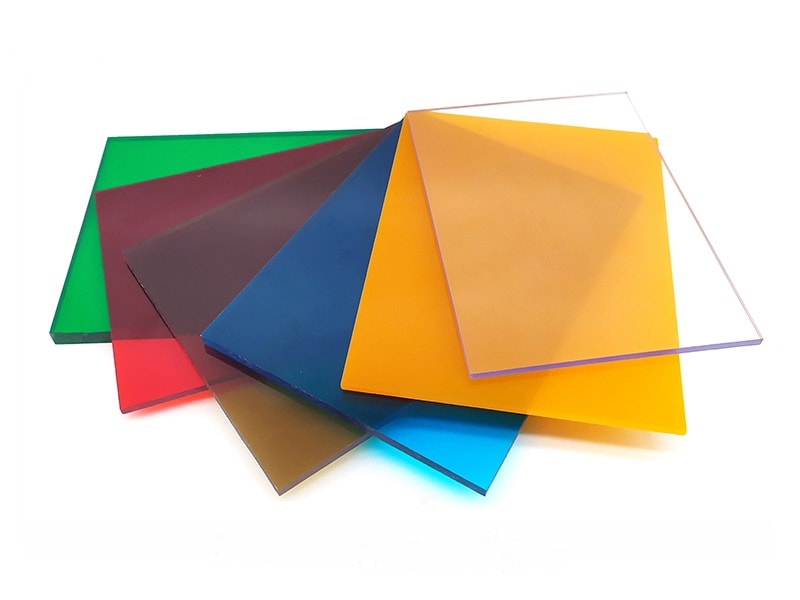
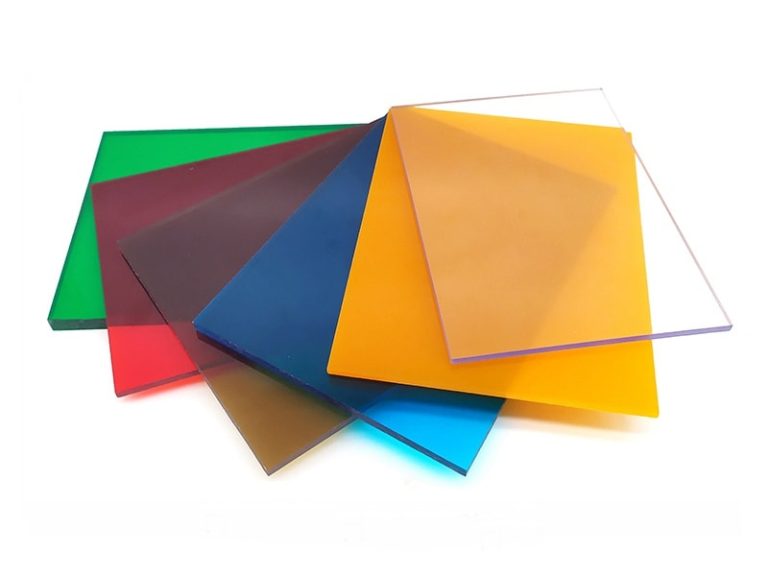
About Polycarbonate sheet
Polycarbonate Sheet is made of polycarbonate plastic by extrusion process, the thickness is from 1mm to 20mm. The natural color is transparent, but it can be produced with custom colors, for example, blue, green, white, red, Grey, etc. The main features include excellent impact resistance, good optical properties, and extraordinary durability.
Polycarbonate sheet is virtually unbreakable, it is 20-30 times stronger than plexiglass sheets, and 25 times stronger than tempered glass. The normal polycarbonate sheet offers flame retardance with V2/UL94, but it can be V0/UL94 with more flame retardants.
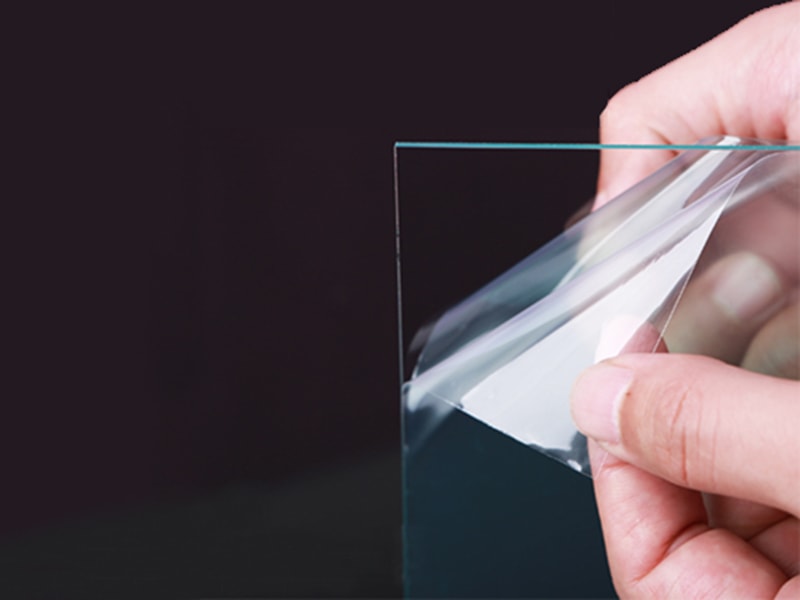
The disadvantage of polycarbonate sheets is that the surface is scratched easily, but with the surface coating technology, it is dramatically improved. Otherwise, there are many different grades of polycarbonate sheets for different applications, for example, ESD/anti-static, scratch-resistant, anti-fogging, UV-blocking, IR-blocking, Anti-glare, glass-filled, etc.
As one of the popular engineering plastics, polycarbonate sheets are used frequently for machine guards, windshields, front plates of electric devices, riot shields, bullet-proof glass, face shields, some transparent parts, building materials, and industrial parts, etc.
UVTECOTM Polycarbonate sheet
Polycarbonate Sheet in stock
Polycarbonate sheet offers excellent impact resistance, great light transmittance, and good fire resistance. With surface coating technology, it can be endowed with one or multiple functions, for example, Scratch-resistant polycarbonate, ESD/anti-static polycarbonate, and Anti-fog polycarbonate, etc.
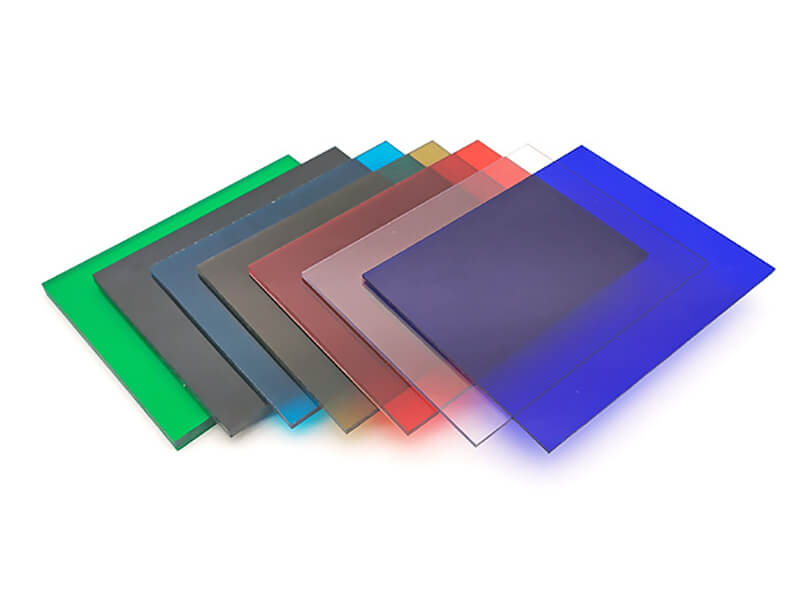
available Colors of polycarbonate sheet
The natural color of polycarbonate sheets is transparent, but UVTECO can make custom colors by adding the color Masterbatch, which is an environmentally friendly annexing agent. Otherwise, UVTECO stock polycarbonate sheets with the common colors for fast delivery.

Clear 
White 
Black 
Gray 
Brown 
Yellow 
Blue 
Green 
Red
| No. | Color | Type | Light transmittance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clear | Transparent | 85% |
| 2 | White | Opaque | 0% |
| 3 | Black | Opaque | 0% |
| 4 | Gray | Translucent | 49% or 35% |
| 5 | Brown | Translucent | 17% |
| 6 | Yellow | Translucent | 80% |
| 7 | Blue | Translucent | 38% |
| 8 | Green | Translucent | 50% |
| 9 | Red | Translucent | 12% |
Properties of Polycarbonate sheet
As one of the popular engineering plastic sheets, polycarbonate sheets offer great physical properties and excellent machinability, it is the best material for machine guards, security glass, windshields, and roofing materials of buildings, etc.
Main Usage of Polycarbonate Sheet
Main Feature of Polycarbonate sheet
Can’t find what you need? Or need a custom polycarbonate sheet?
Leading Supplier of Polycarbonate Sheets in China
As a leading supplier of polycarbonate sheets in China, UVTECO is stocking polycarbonate sheets in different grades and common colors for fast delivery to global clients. Otherwise, UVTECO can machine polycarbonate sheets by different processes, including cutting, bending, drilling, rapid prototype, 3-axis & 5-axis CNC milling, CNC Turning, injection molding, thermal forming, silk-screen/UV printing, engraving, polishing, coating, electroplating, coating, etc.
UVTECO is one of the wholly-owned subsidiaries of UVPLASTIC, which has been active in the engineering plastic field since 1995 and began to manufacture polycarbonate sheets in 2003. Today, UVTECO is providing high-quality polycarbonate sheets, parts, and components for more than 2500 clients from more than 45 countries, they are working in the automobile industry, machine vision, inspection equipment, medical device, food machinery, metaverse, aerospace industry, safety equipment, security glass, agriculture, architecture, etc.
Contact UVTECO for machining Polycarbonate service
Frequently Asked Questions about Polycarbonate Sheet

Contact UVTECO
Have questions or need help? Fill out the right form, we will be in touch with you as quickly as possible.