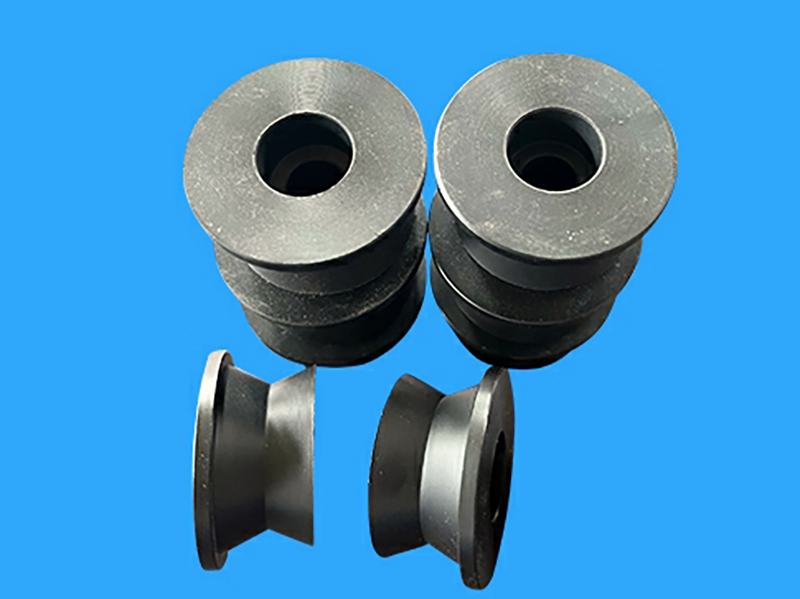
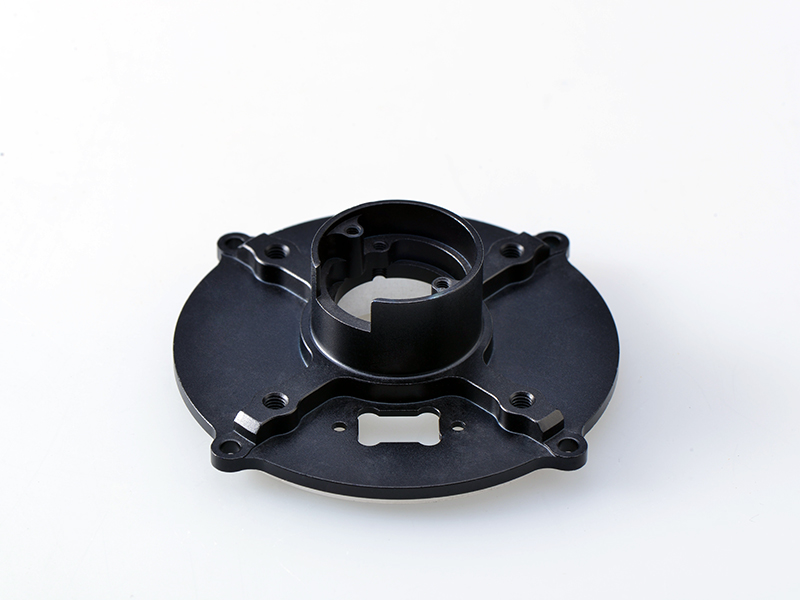
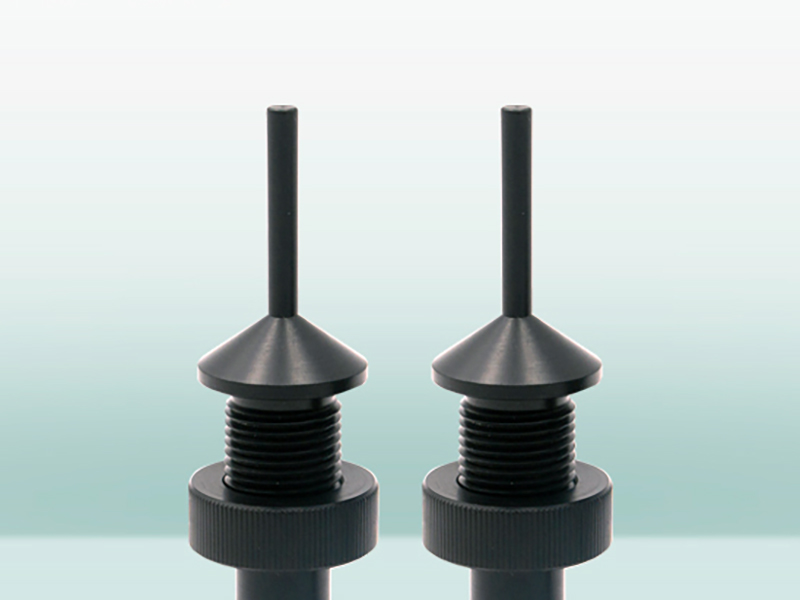
Leading Supplier of Polycarbonate Rod And Machining Service
Polycarbonate Rod and Turning-lathe Machine it
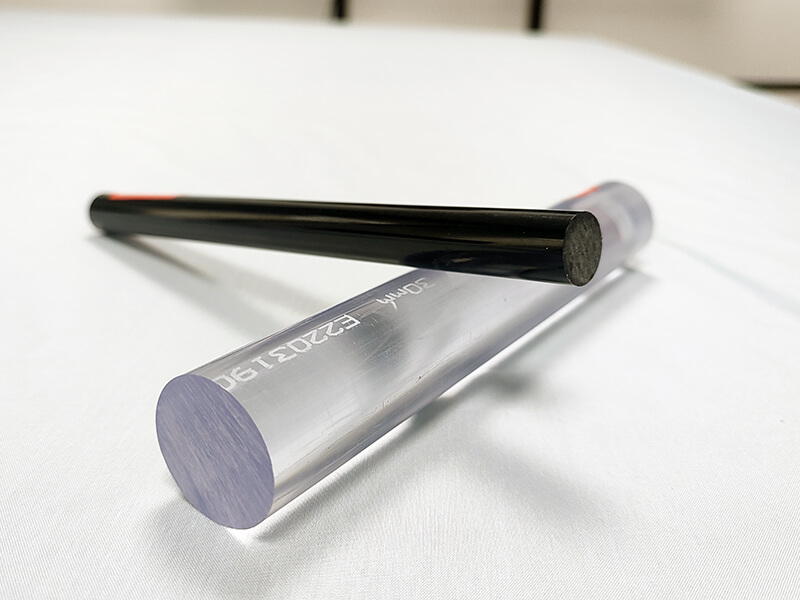
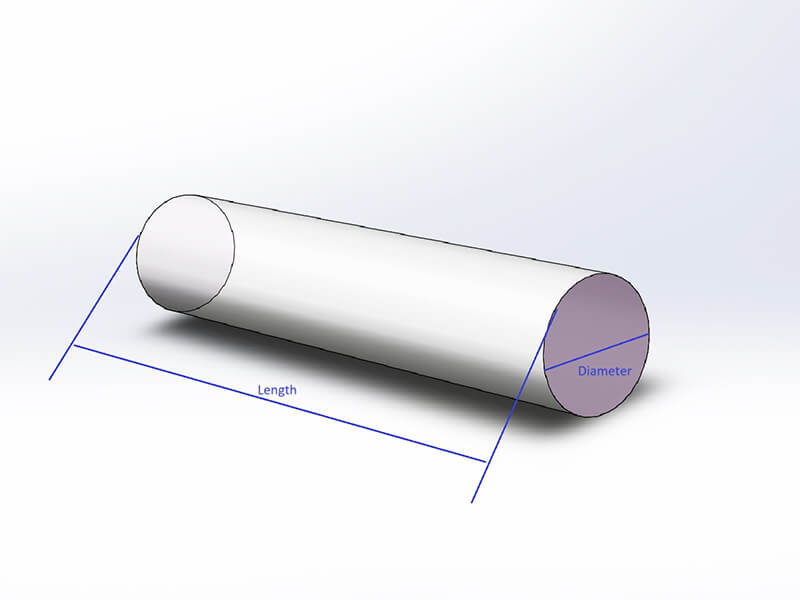
Polycarbonate Rod is made of transparent polycarbonate granules by extrusion processing, it is a semi-transparent or black thermoplastic plastic rod with excellent machinability, high impact resistance, and excellent electrical properties. In addition, polycarbonate rod offers a low water absorption rate and good chemical resistance.
As one of the popular engineering plastic rods, polycarbonate rod is different from acrylic rod, it offers higher impact resistance, better dimensional stability, and good strength and stiffness over a wide range of temperatures -40°C to 120°C, but the light transmittance is lower, therefore, polycarbonate rods are used frequently for industrial applications.
UVPLASTIC is a leading manufacturer and wholesaler of polycarbonate rods in China, we supply and wholesale polycarbonate rods with diameters from 6mm to 300mm. In addition, we can make custom polycarbonate rods and machine them by saw and turning-lathe machines.
Specification Of Polycarbonate Rod
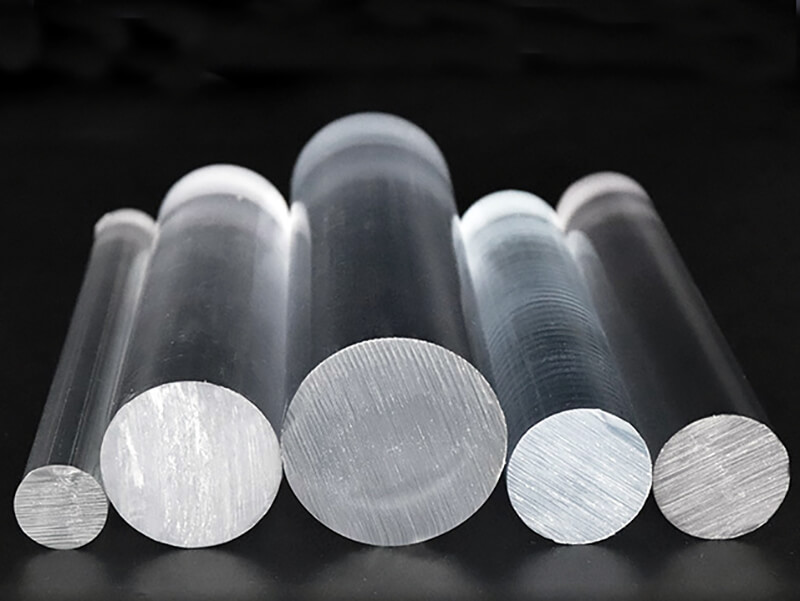
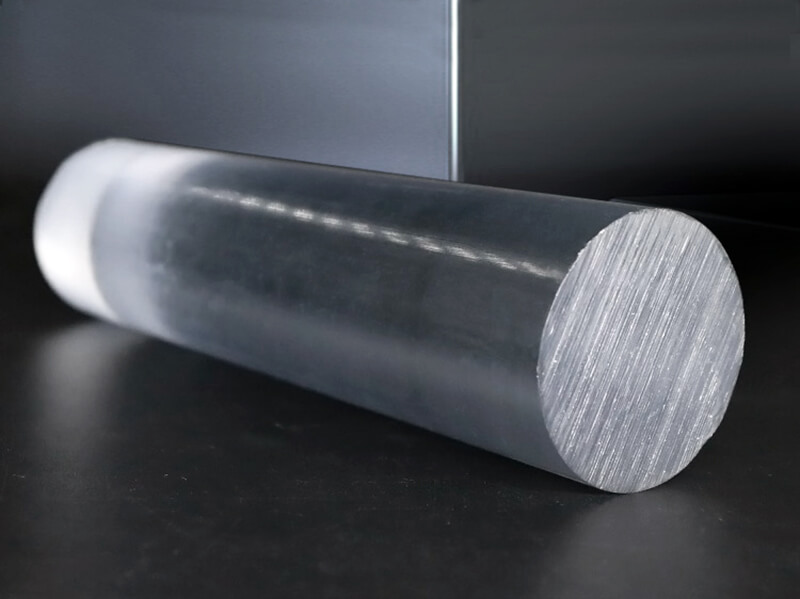
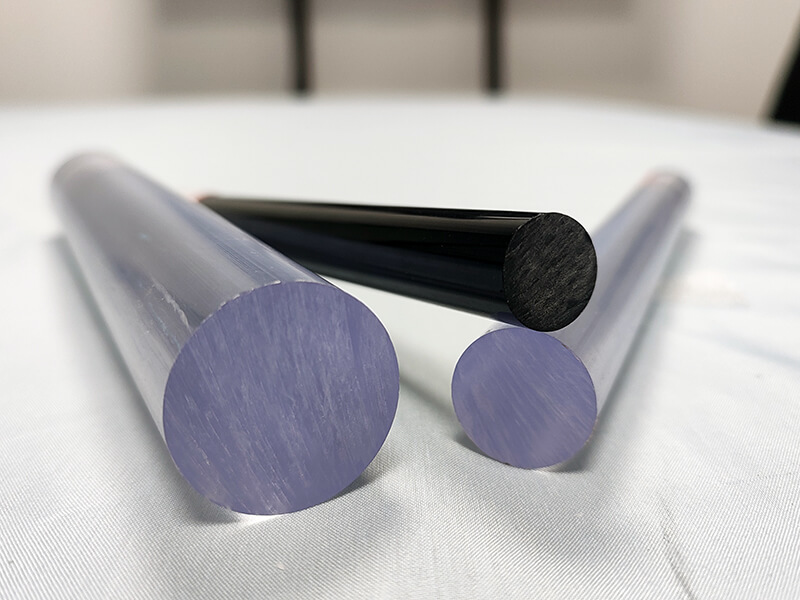
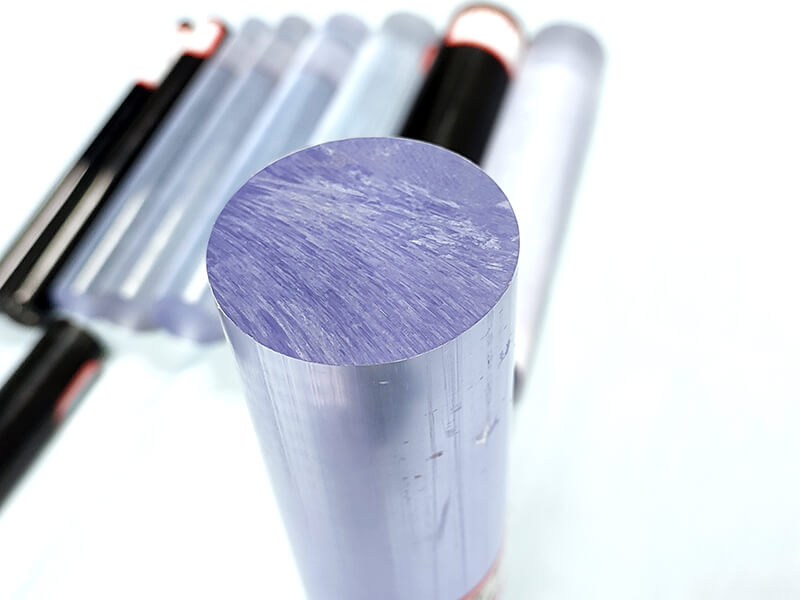
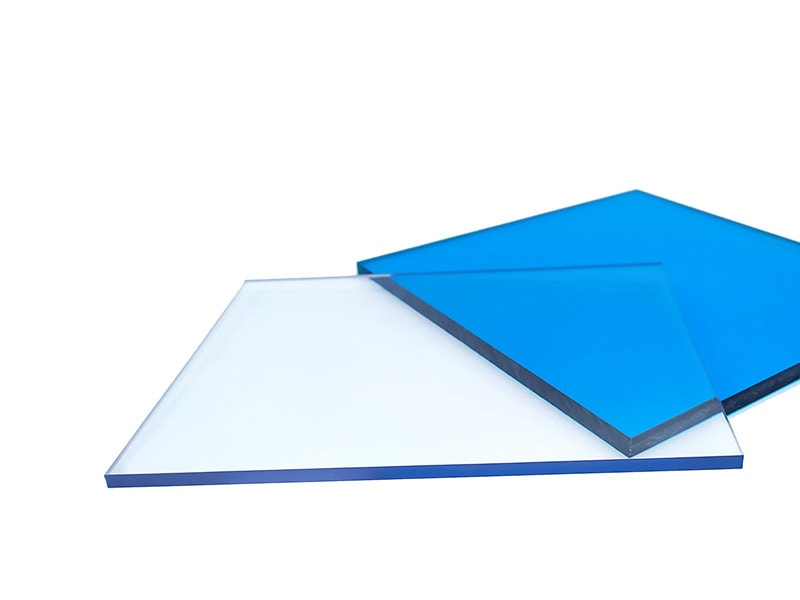
UVPC-ROC Clear polycarbonate Rod
UVPLASTIC supplies clear polycarbonate rods with diameters from 10mm to 300mm, it offers good machinability, high impact resistance, and excellent electrical properties. Normally, it will be machined into parts by turning-lathe machine for industrial applications.
Remark
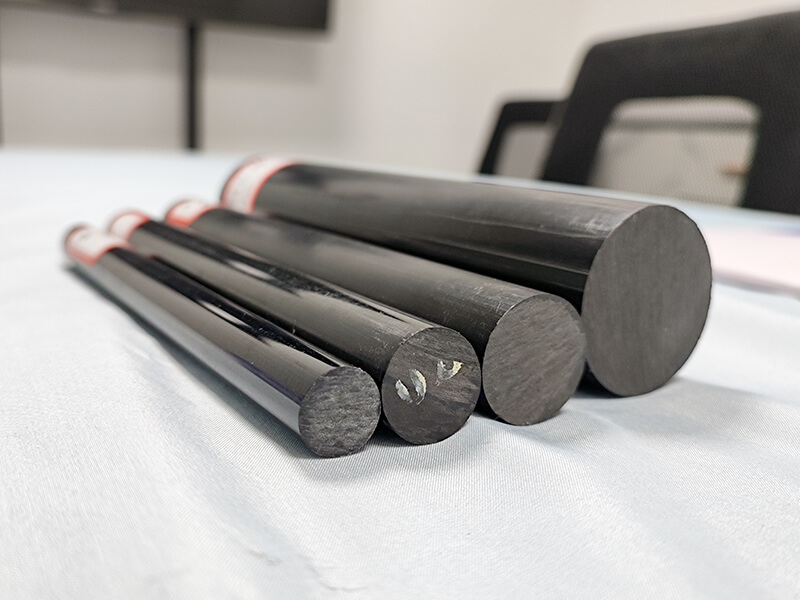
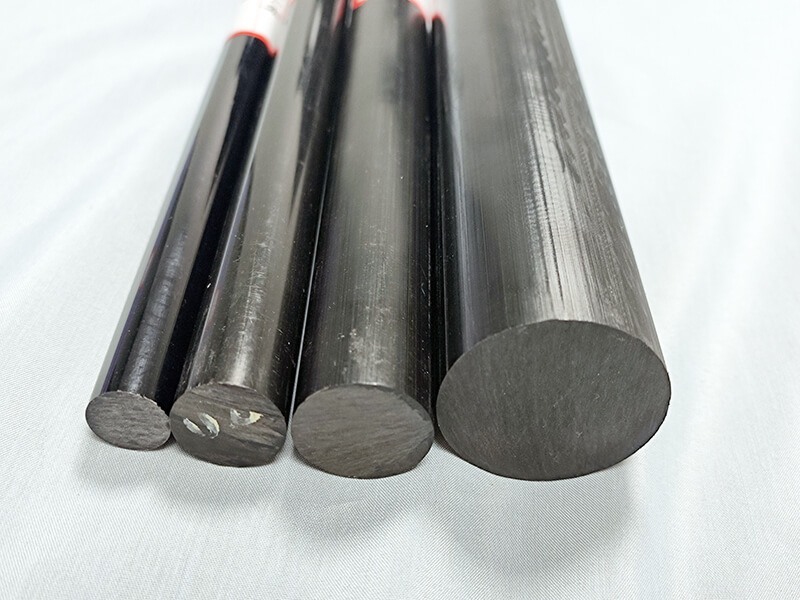
UVPC-ROB Black polycarbonate Rod
Black polycarbonate rod is made of polycarbonate granules, master-batch color, and 30% glass fiber, it offers excellent machinability, high impact resistance, and low water absorption.
Typic applications
Physical Properties of Polycarbonate Rods
| Property | Test Method | Testing Condition | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | D-792 | g/cm3 | 1.2 | |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | D-648 | Load: 1.82 MP | °C | 135 |
| Short Time Service Temperature | °C | from -50 to +130 | ||
| Long Time Service Temperature | °C | from -40 to +100 | ||
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion | D-696 | mm/m °C | 0.065 | |
| Thermal Conductivity | C-177 | W/m K | 0.21 | |
| Tensile Strength at Yield | D-638 | 10 mm/min | Mpa or N/mm² | >65 |
| Tensile Strength at Break | D-638 | 10 mm/min | MPa or N/mm² | >60 |
| Elongation at Yield | D-638 | 10 mm/min. | % | 6 |
| Elongation at Break | D-638 | % | >95 | |
| Tensile Modulus of Elasticity | D-638 | 1 mm/min | MPa | 2350 |
| Flexural Strength | D-790 | 1.3 mm/min. | MPa | 100 |
| Flexural Modulus | D-790 | 1.3 mm/min. | MPa | 2600 |
| Impact Falling Weight | ISO 6603/1 E50 | 3mm sheet | J | 158 |
| Flammability rate | UL 94 | V-2 or V-0 |
The default third-party testing organization is SGS;
Main Benefits

UL Flammability Standard Released By Underwriters Laboratories
UVPLASTIC Polycarbonate Rod can meet the V-2 fire rating according to UL94
Restriction Of Hazardous Substances
UVPLASTIC offers environmentally-friendly polycarbonate sheets and meets RoHS and REACH