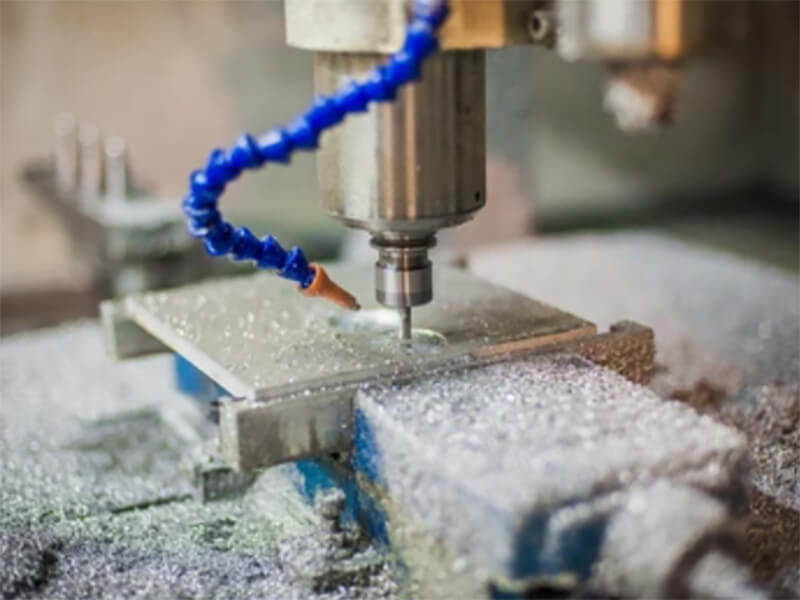
everything comes FROM material AND machining SOLUTION
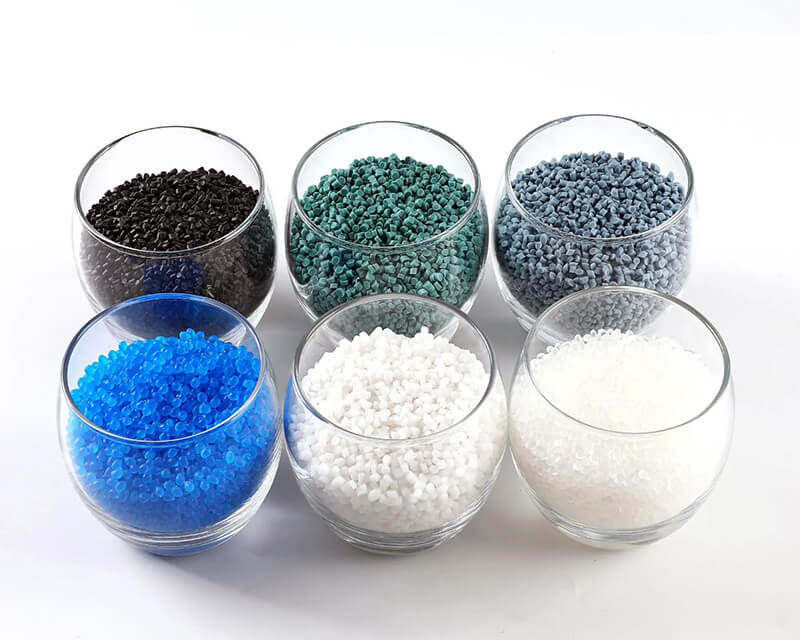

New Material R&D
UVTECO is Working with Global Clients for New materials, which offer particular properties.

Materials
UVTECO is a top manufacturer & distributor of Engineering Plastic, Foam & Sponge, Rubber, Metal, etc.
UVTECO material range
Material in stock for fast delivery
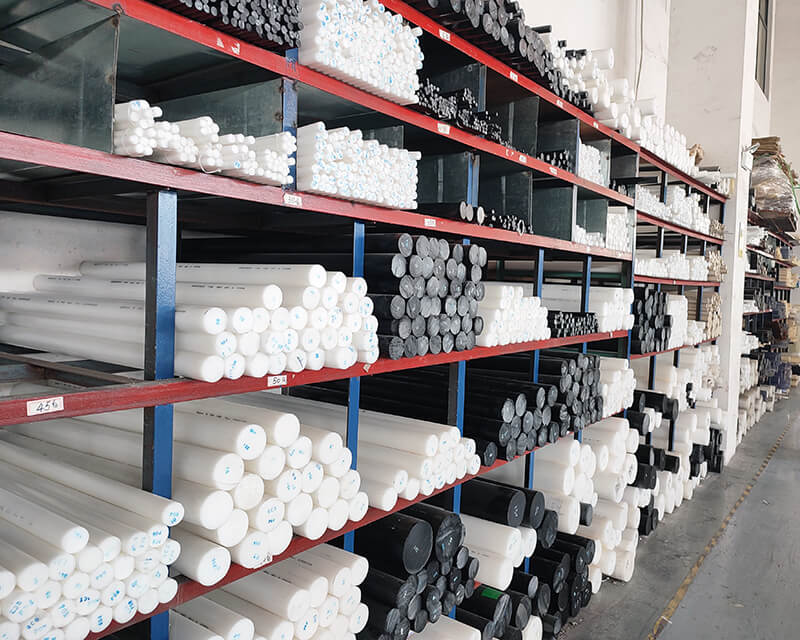
UVTECO stocks Engineering Plastic, Foam, Rubber, Metal, etc, which are used frequently for industrial parts/components. In this case, we can deliver these materials to global clients quickly.
Engineering plastic
Sheets, Blocks, Films, Rods, and Tubes made by PC, PP, PMMA, PA, PEEK, etc.
Foams & Sponge
Conductive Foam, ESD Foam, EVA Foam, Silicone Foam, Neoprene Sponge Foam, Polyurethane Foam, Elastomeric Foam, PE Foam, etc.
rubber
Neoprene Rubber, EPDM Rubber, Nitrile Rubber, Silicone Rubber, SBR Rubber, etc.
Metal
Alloy Steel Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Copper, Silver, Gold, etc.
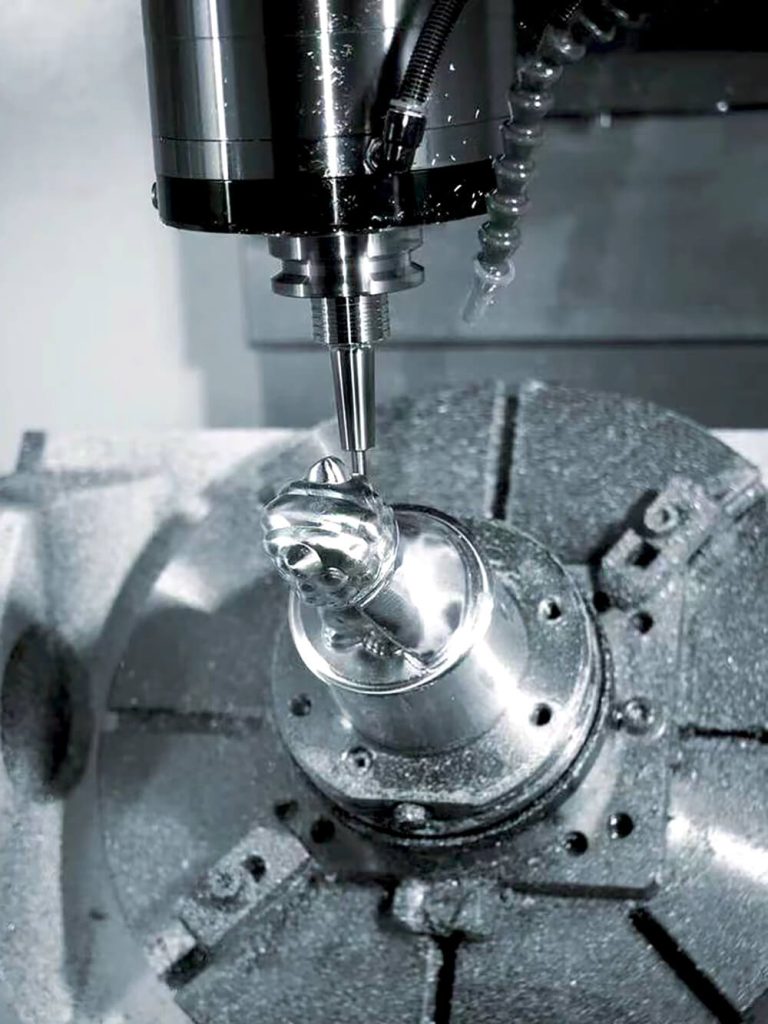

Custom Manufacturing From Designing to High-Volume Production
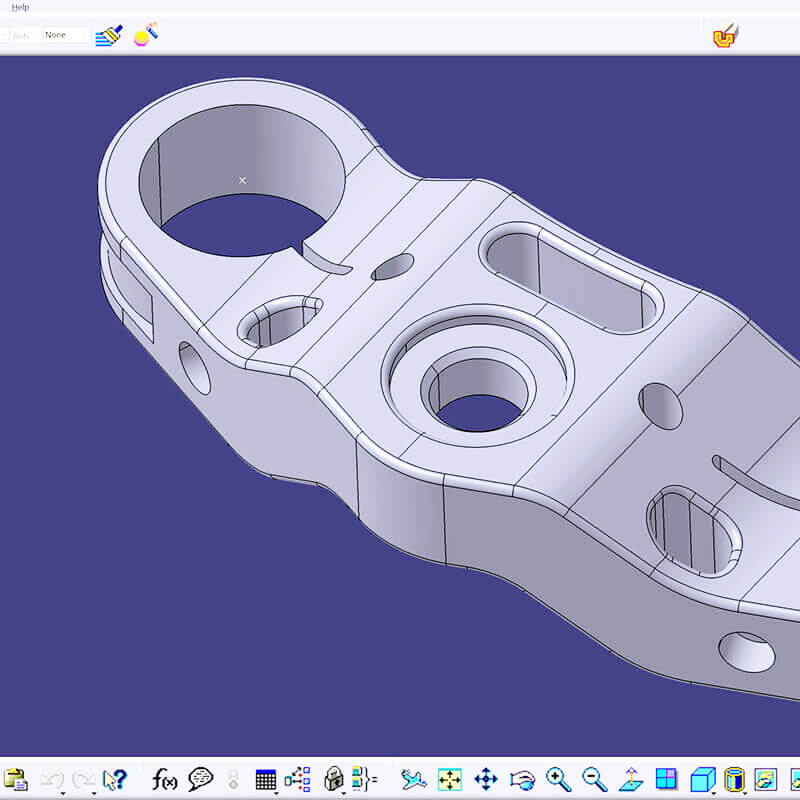
Industrial Parts Design
By Using Software including SolidWorks, UG, and CATIA, we work with global clients to design components.
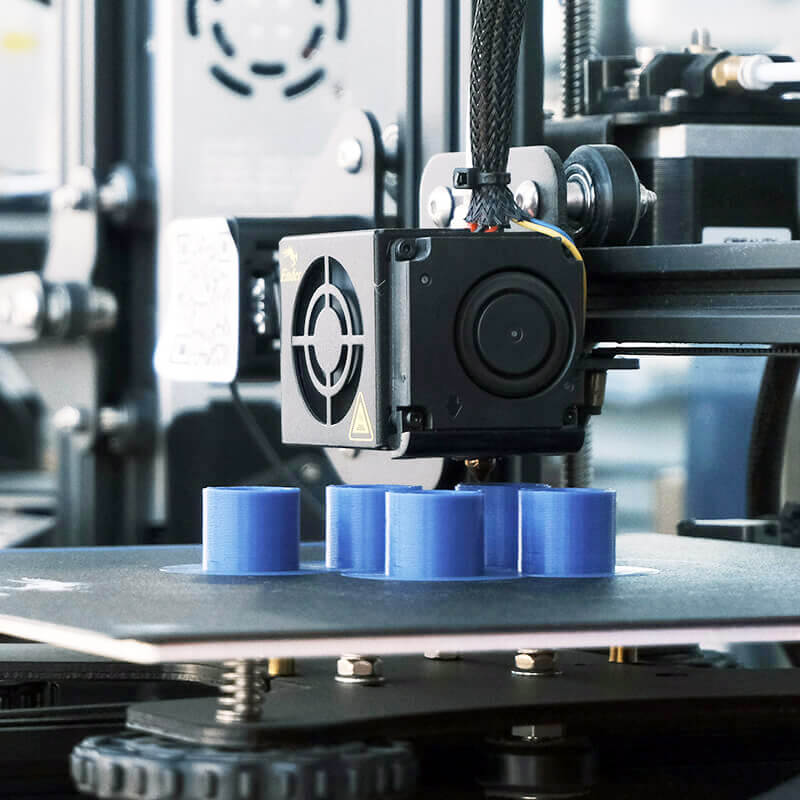
Rapid Prototyping
UVTECO provides ONE-STEP rapid prototyping services to support every process of product development from the global market.
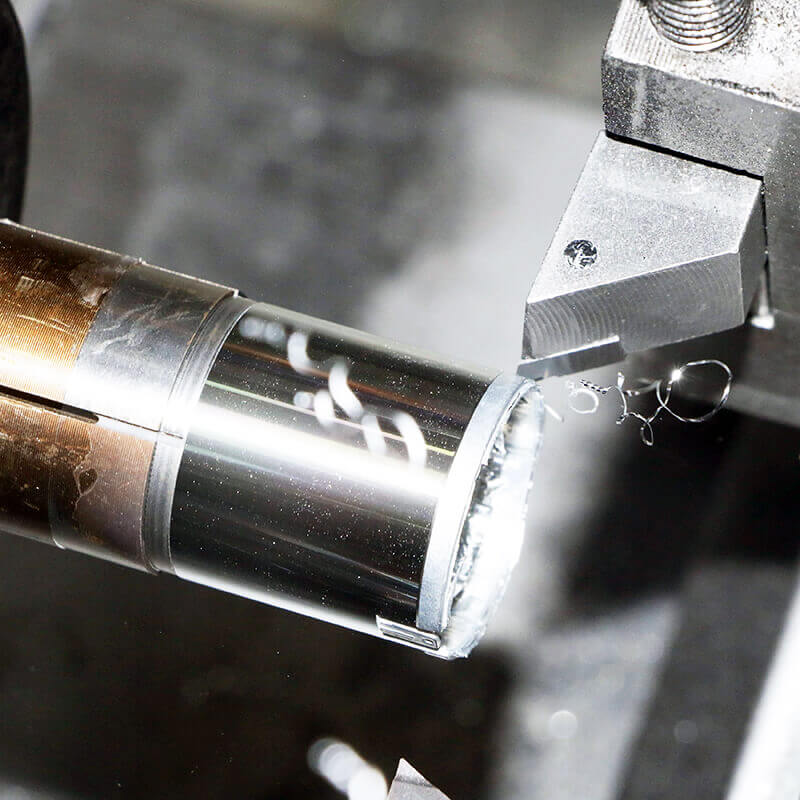

Low-Volume manufacturing
UVTECO helps global clients get to market faster by providing cost-effective and fast low-volume manufacturing services.
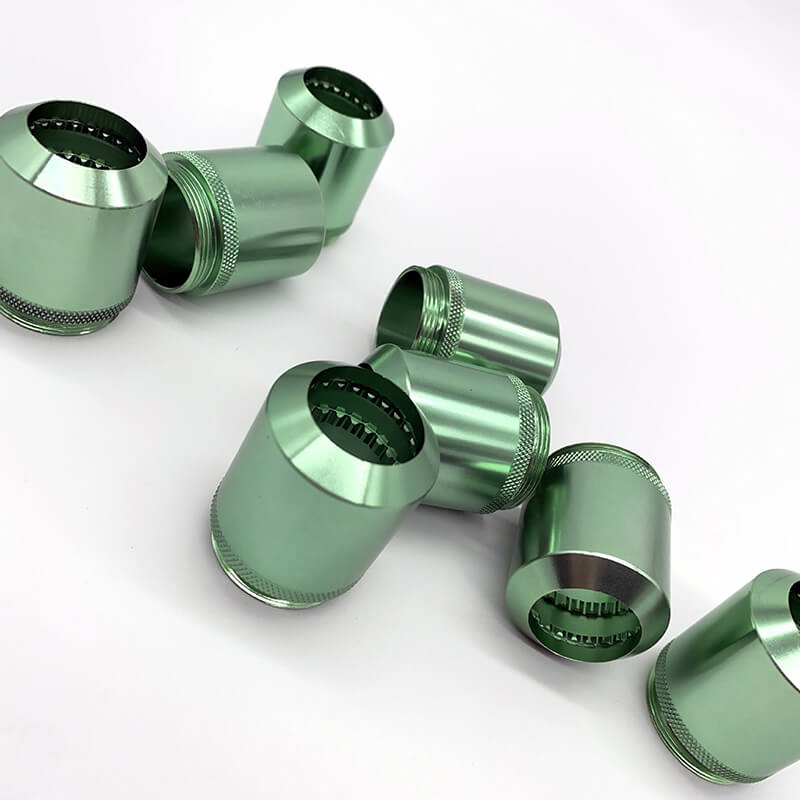

high-volume production
With knowledge and experience in materials and machining processes, UVTECO provides OEM services for high-volume production.
KNOW MATERIAL, KNOW MACHINING
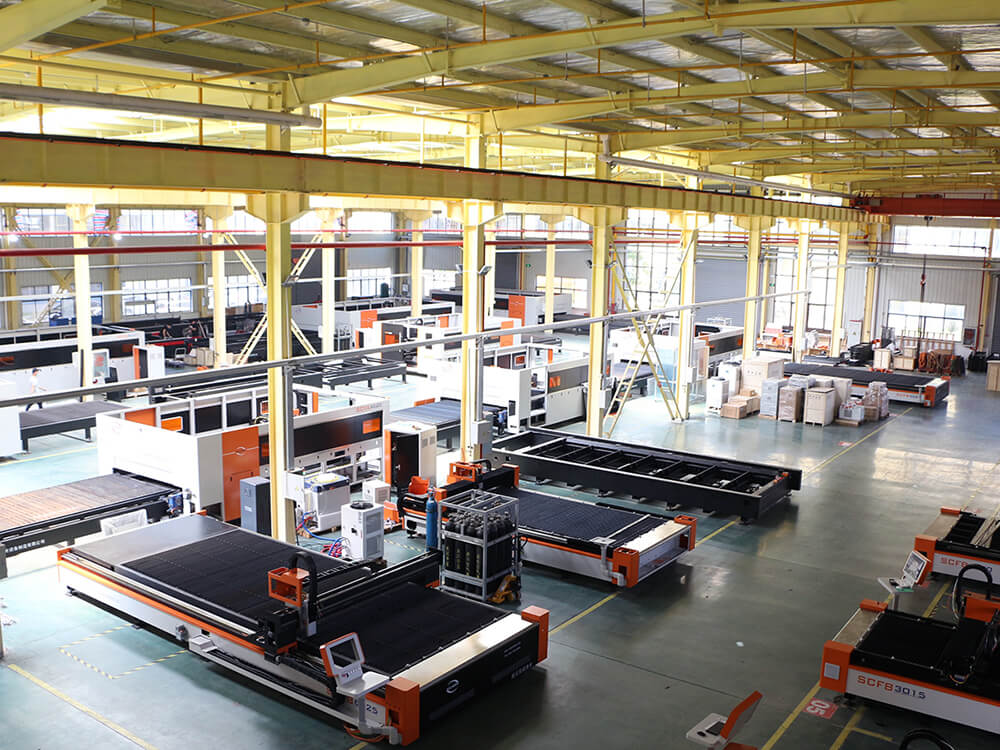

our advantage
your right partner for parts/components
With more than 30 years of experience in the industrial field, UVTECO has grown to be a leading supplier of materials and provider of OEM services for industrial parts.
UVTECO offers comprehensive capabilities including in-house machining and integration of manufacturing resources in China. We are always ready to support you with not only suitable materials but also integrated machining solutions.
our Clients
what our clients say
With high-quality products and superior service, we are working with more than 2000 clients from more than 40 countries.

Thomas Kruck
Munich, Germany
“UVTECO supplied Polycarbonate Diffuser Parts, which will be used as a part of the PHUD, we are very happy with them, and will order more in the future.”

Tsugumi Susaki
Tokyo, Japan
“We ordered Aluminum Parts in low volume, we are very excited about the fast delivery and good quality, UVTECO helps us to get more orders from our clients.”

Carrié Charles
Paris, France
“We have been working with UVTECO for more than 9 years, I am very impressed with their high efficiency and professional in material and machining capability.”

Norman Engel
Texas, America
“We are very happy to work with UVTECO because they provided very cost-effective parts, and saved lots of cost by developing new materials for our projects.”
industries we are working for
 Agriculture
Agriculture Aircraft & Aerospace Industry
Aircraft & Aerospace Industry Automation Equipment
Automation Equipment Automobile Industry
Automobile Industry Construction Industry
Construction Industry Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics Green Energy Industry
Green Energy Industry Home Appliance
Home Appliance Medical Industry
Medical Industry Metaverse
Metaverse Military Equipment
Military Equipment Recreational Machines
Recreational Machines Semiconductor Industry
Semiconductor Industry Telecommunications
Telecommunications Energy Industry
Energy Industry


